What is Astaxanthin good for?
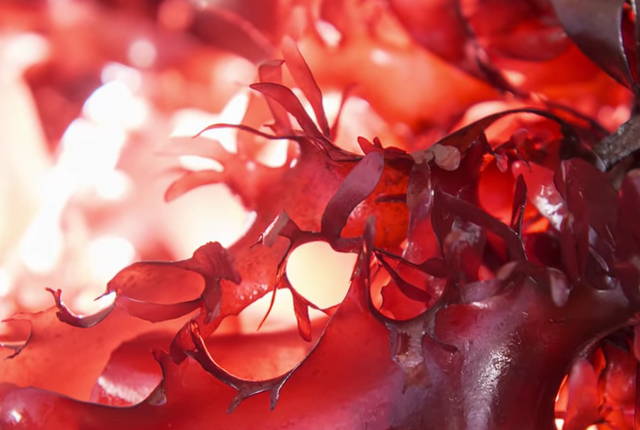
Have you ever wondered why some sea creatures are pink? Their red or pinkish hue comes from the ketocarotenoid astaxanthin (“asta-xan-thin”), a high-value pigment with antioxidant properties. As curiosity increases around astaxanthin’s benefits—especially in skincare—research continues to unravel its potential.
How can a pigment such as astaxanthin be so powerful? Although research is still emerging, this ingredient is proving to be a promising addition to modern skincare routines.
What is Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring pigment found in microalgae, yeast, and sea creatures such as salmon and shrimp. Sea animals ingest algae rich in astaxanthin, making them a potent dietary source of antioxidants—one reason salmon is often associated with healthy skin and nutrition.
Astaxanthin’s secret is its small molecular structure, which allows it to cross blood–brain and blood–retina barriers more effectively than many antioxidants. This enhances protection for the brain, eyes, and other vital organs.
Our Moisturizing Caviar Multi-Balm Stick utilizes astaxanthin as a key active ingredient. When applied twice a day, it offers immediate hydration and visibly softens fine lines.
Astaxanthin also supports anti-aging, improves elasticity and texture, and may help reduce concerns such as crow’s feet. If you’re looking for a well-rounded skincare enhancer, astaxanthin is a strong contender.
Early research indicates astaxanthin may improve blood flow, reduce oxidative stress, and even inhibit cancer cell growth. More studies are needed to deepen understanding, but results so far are compelling.
What Are the Health Benefits of Astaxanthin?
- Healthy Skin
Astaxanthin has become popular for its ability to reverse visible signs of aging. Whether applied topically or taken orally, it may reduce wrinkles, age spots, and dryness while improving overall moisture levels.
- Immune System Support
Astaxanthin boosts immunoglobulin (Ig) levels, improves T-cell activation, and helps the body fight off infections and inflammation. These immune-boosting qualities may help defend against chronic inflammatory diseases.
- Increased Endurance
Studies (mostly on animals) show astaxanthin may improve endurance, increase fatty acid utilization, and reduce muscle damage. Human-based research is ongoing, but early results are promising.
Astaxanthin may also help improve heart health by reducing oxidative stress and supporting cardiovascular function.
- Protection from the Sun
When taken orally, astaxanthin helps protect skin from UV damage by strengthening the barrier and supporting DNA repair. Accumulating in both the dermis and epidermis, it reduces long-term sun damage.
NOTE: It does not replace sunscreen—but works even better alongside it.
- Relieves Joint Pain
Early research suggests astaxanthin may help with joint-related pain and inflammation, including conditions such as carpal tunnel syndrome and rheumatoid arthritis.
Health Risks & Side Effects of Astaxanthin
Like any ingredient, astaxanthin may not be suitable for everyone. Individuals with seafood allergies should avoid food-derived sources. Reactions can occur if sensitive to compounds found in shellfish such as shrimp, crab, or lobster.
Astaxanthin may interact with blood pressure medications and is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding without medical approval.
Consult your doctor if you have concerns or experience unusual symptoms.
Summary: What Is Astaxanthin and What Does It Do?
Although research is still growing, astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant that pairs well with most ingredients, enhancing the effectiveness of vitamins C and E.
It can be taken orally or applied topically (up to twice a day), with noticeable results in 2–8 weeks.
As studies continue, astaxanthin is gaining attention for its benefits across all genders and skin types. It’s likely to become a staple ingredient in skincare for years to come.