Read more

Can You Use Lactic Acid With? - Benefits, Pairing , FAQ
Lactic acid is a versatile and effective ingredient when used correctly. By understanding its properties and best pairings, you can unlock its full potential for a radiant and healthy complexion. R...
Read more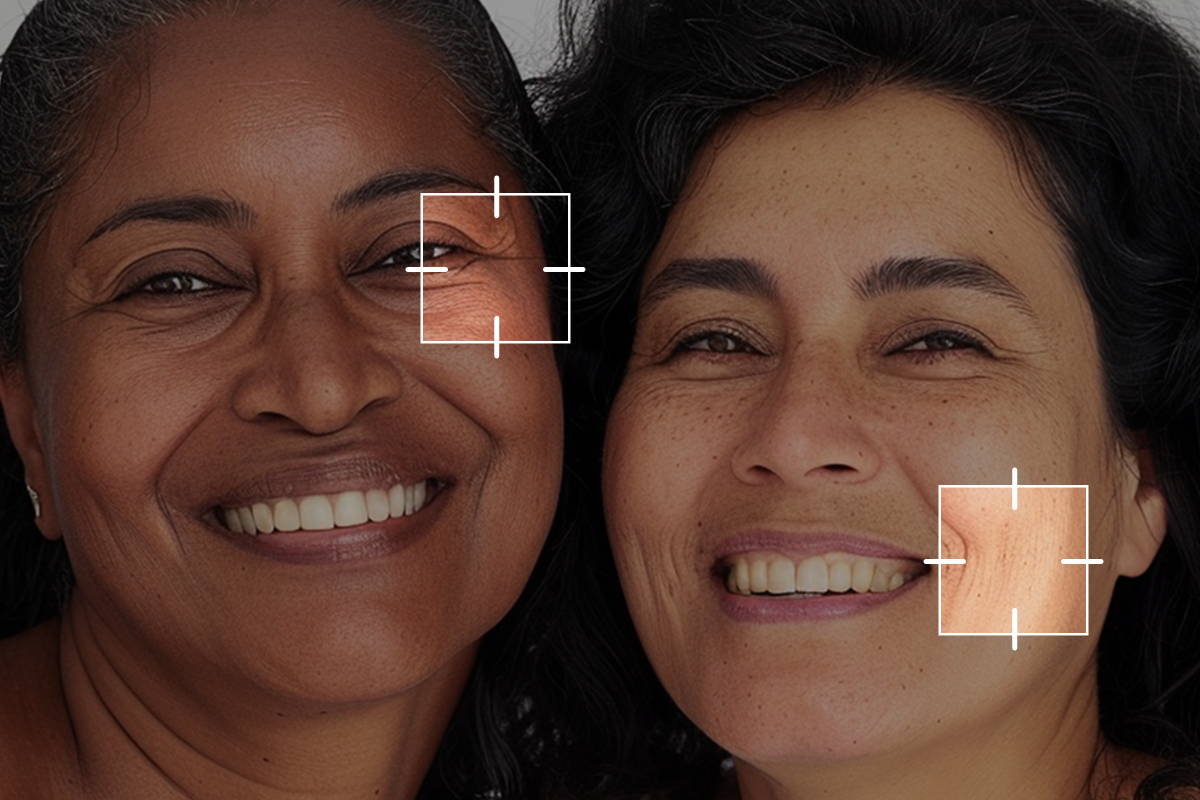
What are Dynamic Wrinkles vs Static Wrinkles?
Discover the difference between static and dynamic wrinkles and learn how Depology's innovative serums can help you target and reduce their appearance. Improve your skin's texture and achieve a mor...
Read more